Melanoma
Although melanoma is less common than other skin cancers, it is the deadliest, accounting for about 75% of all skin cancer deaths. Each year, approximately 160,000 new melanoma cases are diagnosed in the U.S. Excessive ultraviolet (UV) light exposure is a major risk factor for developing melanoma.
Regular Total Body Skin Exams (TBSEs) by a dermatologist are crucial for detecting melanoma early. Dermatologists have the expertise to identify suspicious moles, lesions, or skin changes that could indicate melanoma. Self-exams are equally important, allowing individuals to monitor their skin for any changes in moles' shape, size, color, or the appearance of new spots.
Combining professional evaluations with self-examinations increases the likelihood of early detection. Timely intervention significantly improves treatment outcomes, highlighting the importance of regular dermatologist checks and self-exams for overall skin health.
At Lupton Dermatology, your skin health is our top priority. Our expert providers are dedicated to caring for you and your loved ones throughout their skin wellness journey.
Examples of Melanoma
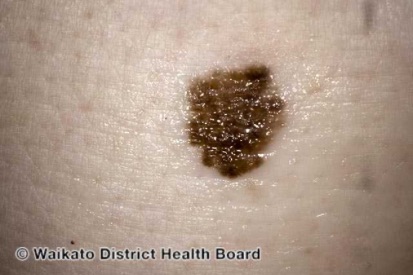
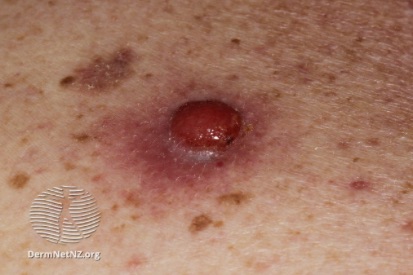
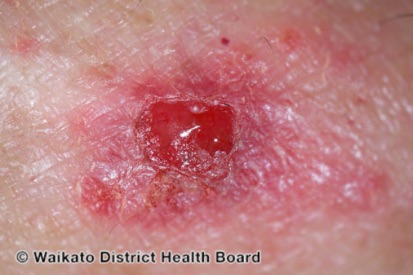
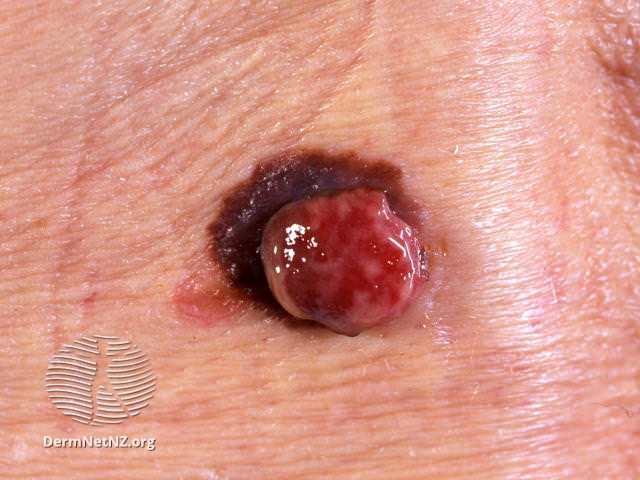
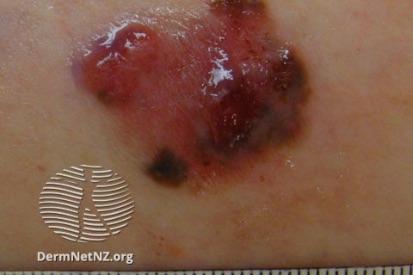
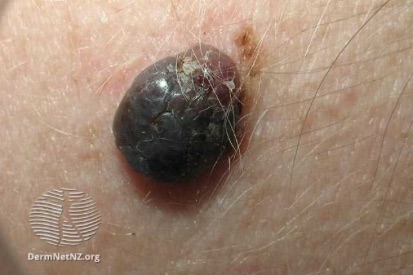
Symptoms of Melanoma
- Melanoma most often presents itself with the change of an existing mole, including change of symmetry, color, or shape.
- Irregular mole borders – scalloped, wavy, or notched.
- Diameter - anything new growing in size.
- Moles that itch, ooze or bleed.
- Melanoma can appear on normal skin tissue and does not always start as a mole.
What Causes Melanoma?
- Melanoma is primarily caused by the uncontrolled growth of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in the skin.
- Melanoma is often triggered by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or tanning beds.
- Genetic factors and a history of severe sunburns also contribute to the development of melanoma.
How to Prevent Melanoma
Melanoma FAQs
The primary cause of melanoma is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from sunlight or tanning beds. Other risk factors include having fair skin, a history of sunburns, numerous moles, a family history of melanoma, and a weakened immune system.
Diagnosis involves a biopsy, where a sample of the suspicious area is removed and examined under a microscope. Dermatologists may use the ABCDE rule (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variations, Diameter larger than 6mm, Evolution or change) to assess whether a mole may be melanoma.
Melanoma is staged from 0 to IV, with stage 0 being melanoma in situ (confined to the top layer of skin) and stage IV indicating the cancer has spread to other organs. Staging helps determine the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions.
Treatment options for melanoma depend on the stage of the cancer and may include surgical excision, lymph node removal, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. The choice of treatment is individualized based on factors such as the patient's overall health and the characteristics of the melanoma.
A skin check performed by a dermatologist involves a thorough examination of the skin to identify any abnormalities, including moles, lesions, or other signs of skin conditions or skin cancer. This examination may be part of a routine check-up or may be prompted by specific concerns. The dermatologist assesses the size, shape, color, and texture of moles, and may perform additional tests or biopsies if necessary for further evaluation. Regular skin checks are essential for early detection and management of skin issues, and, skin cancer.
You should apply sunscreen every day, regardless of weather. Even on cloudy days and during the winter, UV rays can still penetrate the clouds and cause skin damage. Sunscreen needs time to be absorbed into the skin. Apply it at least 15-30 minutes before going outdoors and reapply every two hours.
From Our QualDerm Family of Brands: Melanoma Treatment Options
Melanoma Treatment Options
We will confirm melanoma through a biopsy and pathological examination and then treat appropriately.
Treatment options for melanoma provided by a dermatologist may include surgical procedures to remove the cancerous tissue, such as excision or Mohs surgery. Additionally, your dermatologist may recommend therapies like immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the stage and characteristics of the melanoma. Close monitoring, regular skin checks, and collaboration with other specialists ensure effective treatment and reduce the risk of recurrence.
If you notice unusual growths on your skin as mentioned above, we highly recommend scheduling an appointment with one of our providers. Annual skin checks are essential for early detection.
Early detection and treatment are crucial elements of comprehensive skin cancer care.
Featured Products for Sun Protection

EltaMD UV Daily SPF 40 original
Serious UV protection and superior hydration join forces in this sheer facial sunscreen. EltaMD UV Daily has hyaluronic acid to boost moisture retention and diminish fine lines. This lightweight moisturizer with UV protection can be worn alone or under makeup. Choose from tinted and untinted formulas for use every day. 1.7 oz / 48 g

ZO® Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen SPF 50
For sensitive and post-procedure skin, this lightweight, non-irritating mineral sunscreen, with ZOX12® complex, protects against damaging effects from UVA/UVB and IR-A rays, and from HEV light. Net Wt. 118 g / 4 Oz
